
In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Mirzaa G, Amemiya A, editors. Self management of fatal familial insomnia. Zarranz JJ, Digon A, et al., Phenotypic variability in familial prion diseases due to the D178N mutation. Fatal familial insomnia presenting as psychosis in an 18-year-old man. PMID: 18568368 PMCID: PMC2583437.ĭimitri D, Jehel L, Dürr A, Lévy-Soussan M, Andreux V, Laplanche JL, Fossati P, Cohen D. Global distribution of fatal familial insomnia: founder or recurrent mutations. Spontaneous mutations in the prion protein gene causing transmissible spongiform encephalopathy. PMID: 18347820.ĭagvadorj A, Petersen RB, Lee HS, Cervenakova L, Shatunov A, Budka H, Brown P, Gambetti P, Goldfarb LG. Molecular evidence of founder effects of fatal familial insomnia through SNP haplotypes around the D178N mutation. Rodríguez-Martínez AB, Alfonso-Sánchez MA, Peña JA, Sánchez-Valle R, Zerr I, Capellari S, Calero M, Zarranz JJ, de Pancorbo MM. Fatal familial insomnia and sporadic fatal insomnia. Khan Z, Bollu PC, Fatal Familial Insomnia, StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL),, PMID: 29489284Ĭracco L, Appleby BS, Gambetti P. Fatal Familial Insomnia: Clinical Aspects and Molecular Alterations. Llorens F, Zarranz JJ, Fischer A, Zerr I, Ferrer I. Understanding Prion Strains: Evidence from Studies of the Disease Forms Affecting Humans.

Epidemiological characteristics of human prion diseases. While some of presented terapeutic approches appers promising, all of them require profoud research.Ĭhen C, Dong XP. The prime issue is to develop functioning therapeutic or preventive treatment. Subsequent researches are essential to improve understending of fatal familial insomnia. immunotherapy or doxycycline usage.Ĭonclusions. However, there are a number of therapeutic options currently under investigation, e.g.
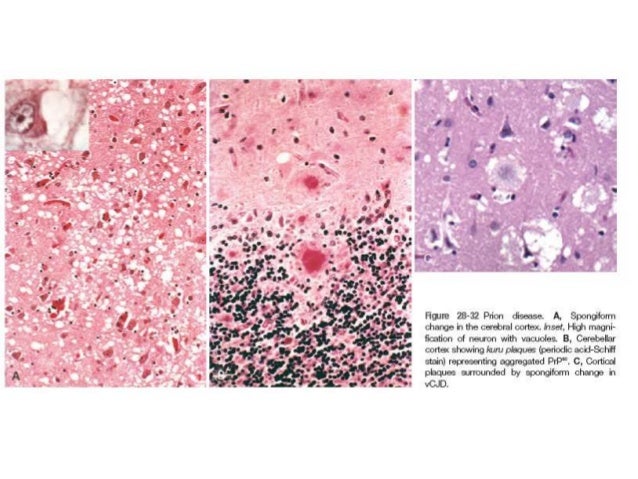
Hence molecular mechanisms involved in pathogenesis are poorly understood, the disease is incureable yet. Average survival time after the onset of symptoms is 18 months. Major vulnerable regions in FFI are mediodorsal and anterior ventral nuclei of the thalamus. The causative agent of this disease is a misfolded version of the physiological prion protein called PrP(Sc) in the brain. The aim of this study is to review the literature and systematize knowledge about fatal familial insomnia.īrief description of the state of knowledge. It is fatal autosomal dominant prion disease, which is extremaly rare- FFI affects only about one person per milion annually. Fatal familial insomnia (FFI) is one of the transmissible spongiform encephathalopathies characterized by neuronal loss, sleep impairment, subsequent non-specific disturbances of autonomic nervous system (e.g. Prion diseases, fatal familial insomnia, neurodegeneration, FFI treatment, prion Abstract Student Research Circle at the Chair and Department of Epidemiology and Clinical Research Methodology, Medical University of Lublin


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
